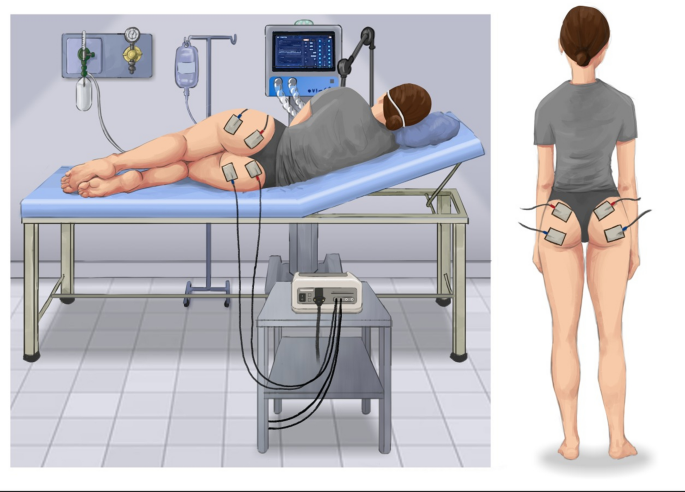
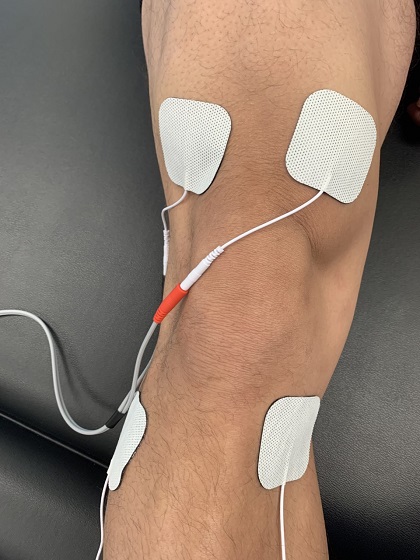
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation to improve exercise capacity in patients with severe COPD: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Neuromuscular electrical stimulation to improve exercise capacity in patients with severe COPD: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Neuromuscular electrical stimulation to improve exercise capacity in patients with severe COPD: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Full article: Effectiveness of neuromuscular electrical stimulation for the rehabilitation of moderate-to-severe COPD: a meta-analysis

Neuromuscular electrical stimulation to improve exercise capacity in patients with severe COPD: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Pulmonary rehabilitation outcomes in individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review - ScienceDirect

JPM, Free Full-Text

Neuromuscular electrical stimulation to improve exercise capacity in patients with severe COPD: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
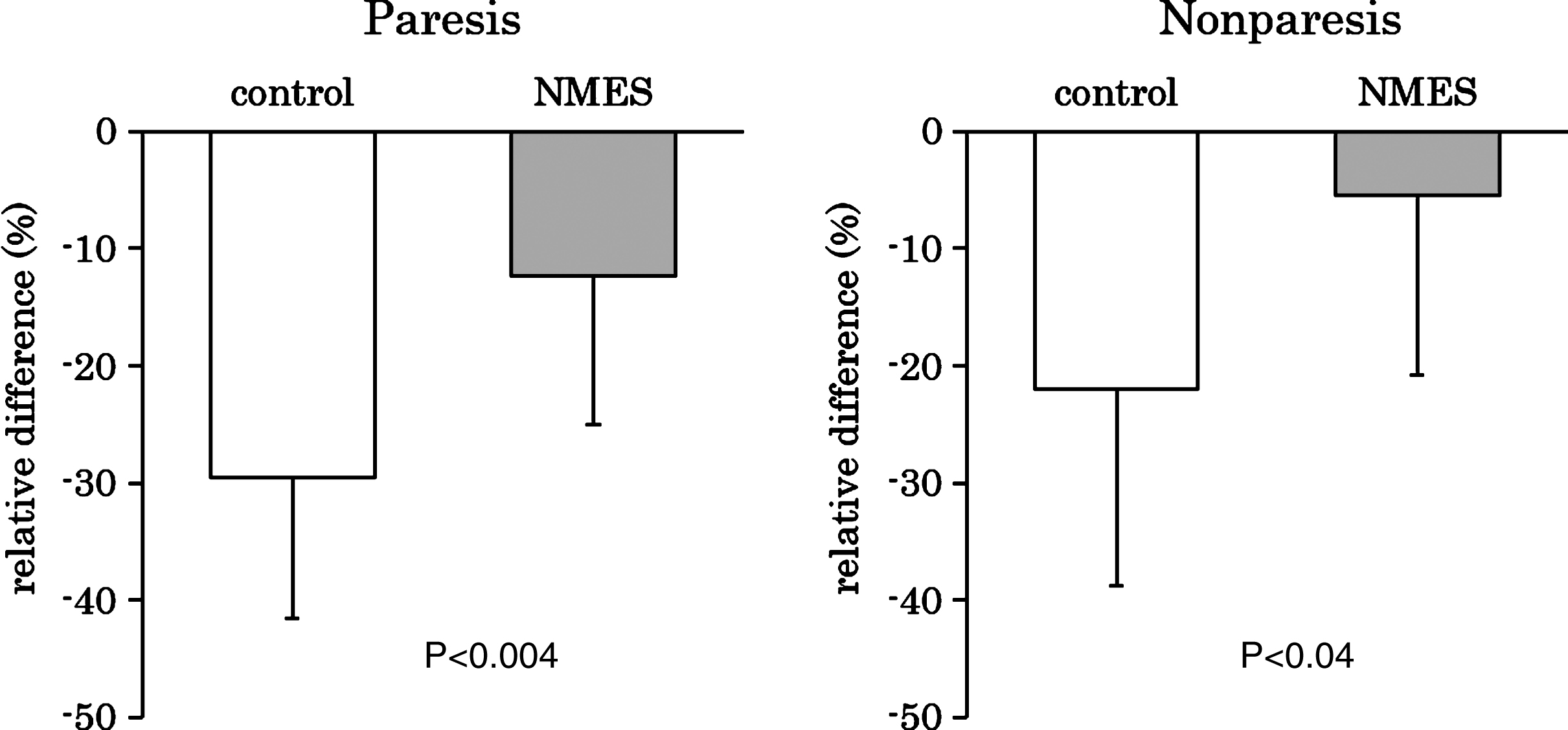
Efficacy of neuromuscular electrical stimulation for preventing quadriceps muscle wasting in patients with moderate or severe acute stroke: A pilot study - IOS Press

Pulmonary rehabilitation and physical interventions
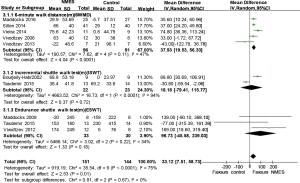
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation improves exercise capacity in adult patients with chronic lung disease: a meta-analysis of English studies - Gong - Journal of Thoracic Disease
Shortness of Breath and Cough in Patients in Palliative Care (19.08.2013)

Musculoskeletal Disorders in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
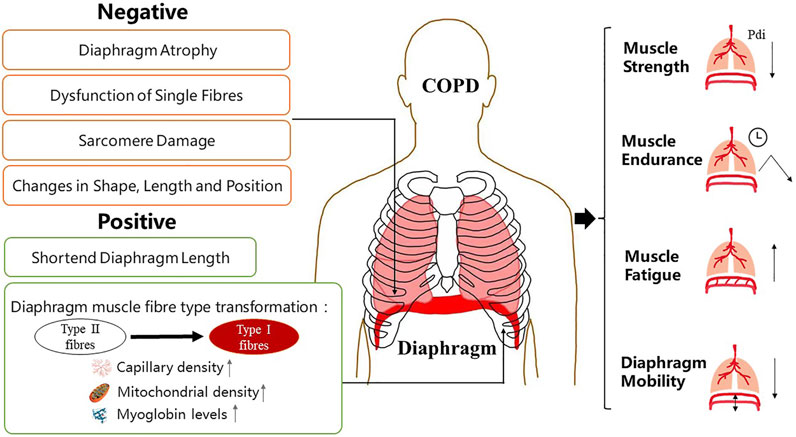
Frontiers Diaphragm Dysfunction and Rehabilitation Strategy in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
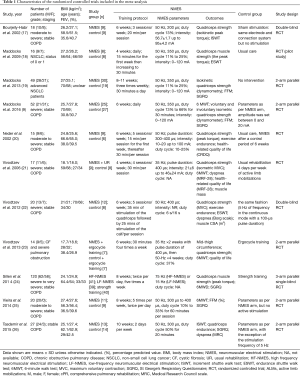
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation improves exercise capacity in adult patients with chronic lung disease: a meta-analysis of English studies - Gong - Journal of Thoracic Disease
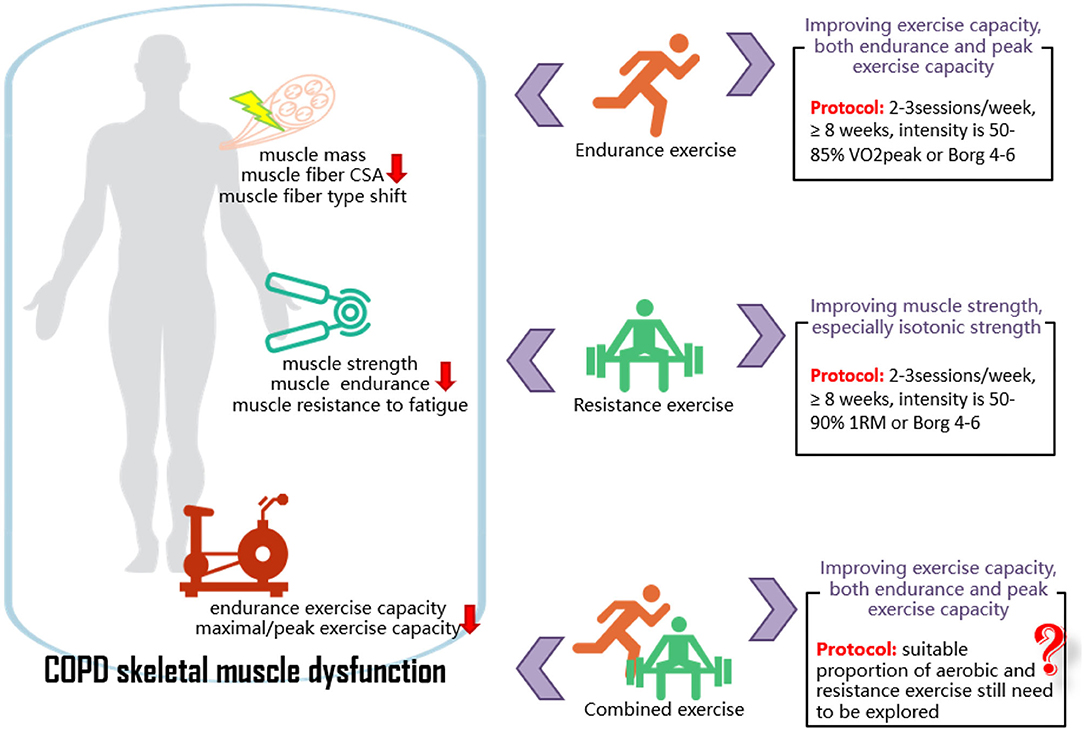
Frontiers Effects of Exercise Intervention on Peripheral Skeletal Muscle in Stable Patients With COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

Full article: Neuromuscular electrical stimulation combined with exercise decreases duration of mechanical ventilation in ICU patients: A randomized controlled trial